I have been working in PostgresSQL and REST API for a long time. So as a challenge I decided to create an API in rails with GraphQL using MongoDB.
As now in most of my development I use Docker, so this project will also contain Docker.
I will be using MongoID and a GraphQL-rails gems to create this app and will be using JWT token authentication for authenticating user.
This is a simple API in which a user will sign up or sign in, and then he or she can create lists and each list will have many to-dos that can only be seen by the logged-in user, so each user will have to-dos of his or her owned.
Initialise Rails Project in Docker:
First create a folder named todo–app in your working directory then use git init to initialise git in that directory. Next create docker-compose.yml
todo-app/docker-compose.yml
version: "3.7"
services:
mongo-service:
image: "mongo:4.2.8"
environment:
MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME: root
MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD: example
ports:
- "27017:27017"
volumes:
- "mongodb:/var/lib/mongodb/data"
rails-api:
build: ./rails-api
environment:
- PORT=3000
volumes:
- ./rails-api:/rails-api:delegated
- rails_log:/rails-api/log
# don't mount tmp directory
- /rails-api/tmp
- ./rails-api/storage:/rails/storage
ports:
- "3000:3000"
depends_on:
- mongo-service
volumes:
mongodb:
rails_log:
This file will create mongo-service in docker and attach to rails. Next it will assume there is a rails-api folder in todo-app where rails code will be present.
Now create a folder inside todo-app named rails-api and create a file named Dockerfile and add the following content:
todo-app/rails-api/Dockerfile
FROM ruby:2.6.6
WORKDIR /rails-api
COPY Gemfile Gemfile.lock ./
RUN mkdir -p log && touch log/development.log
RUN gem install bundler
RUN bundle install
RUN gem install foreman
# Start the main process.
CMD ["foreman", "start", "-f", "Procfile"]
This file tells Docker to create an image with ruby 2.6.6 and install everything present in Gemfile and Gemfile.lock and then run foreman command.
Now create a file in rails-api named Gemfile with the following content:
todo-app/rails-api/Gemfile
source 'https://rubygems.org'
gem 'rails', '~> 6.0', '>= 6.0.3.1'This file will tell docker to install rails 6 on the ruby image.
Furthermore, now create empty file named todo-app/rails-api/Gemfile.lock. Both these file will be edited when we initialize the rails project in docker.
Now create a Procfile which will be used by foreman to run rails in docker.
todo-app/rails-api/Procfile
web: bundle exec rails s -b 0.0.0.0 -p ${PORT}
logger: tail -f log/development.logFinally, write the following command in terminal of the todo-app that will initialize rails project skipping unit testings as we will use RSpec for testing, skipping ActiveRecord that is used by rails when using SQL.
docker-compose run rails-api rails new . --api --skip-active-record --skip-bundle --skip-test --skip-system-test --force --no-depsNow you will see that rails-api folder is filled with rails files and folders.
Updating Gems to be used in project:
Add some extra gems to your Gemfile that will be used by our project.
bcryptfor encrypting user passwordsmongoidfor mongodb controlsgraphqlfor graphql functionalitiessprocketsversion 3 required for playground of graphqljwtfor jwt user authenticationsgraphql_playground-railsfor graphql playground UIfactory_bot_railsfor generating fake datafakerfor fake name, emails etcrspec-railsRSpec to test models and services
Now in bash terminal first down all instances of current docker-compose and build the docker from the start by entering the following commands:
docker-compose down -vdocker-compose up --build -dNow new instance will be created with all the gems installed with the new ones.
Attaching Mongo with Rails and GraphQL initialisation:
Initialise mongo in rails by the following command in terminal:
docker-compose run rails-api bin/rails g mongoid/configChange hosts and options for both development and test in the mongo config file in rails:
todo-app/rails-api/config/mongoid.yml
development:
# Configure available database clients. (required)
clients:
# Defines the default client. (required)
default:
# Defines the name of the default database that Mongoid can connect to.
# (required).
database: rails_api_development
# Provides the hosts the default client can connect to. Must be an array
# of host:port pairs. (required)
hosts:
- mongo-service:27017
options:
server_selection_timeout: 1
Now initialise graphql in rails by entering in terminal
docker-compose run rails-api rails generate graphql:installAlso add following line in routes of rails to have graphql ui enabled:
todo-app/rails-api/config/routes.rb
mount GraphqlPlayground::Rails::Engine, at: "/graphiql", graphql_path: "graphql#execute"Initialising RSpec:
Write in terminal:
docker-compose run rails-api rails generate rspec:installChange rails_helper.rb with the following code:
todo-app/rails-api/spec/rails_helper.rb
# frozen_string_literal: true
# This file is copied to spec/ when you run 'rails generate rspec:install'
require File.expand_path('../config/environment', __dir__)
ENV['RAILS_ENV'] ||= 'test'
require 'rspec/rails'
require 'spec_helper'
# require 'pundit/rspec'
# require "action_cable/testing/rspec"
include ActiveJob::TestHelper
FactoryBot::SyntaxRunner.class_eval do
include ActionDispatch::TestProcess
end
# Prevent database truncation if the environment is production
abort('The Rails environment is running in production mode!') if Rails.env.production?
# Add additional requires below this line. Rails is not loaded until this point!
# Requires supporting ruby files with custom matchers and macros, etc, in
# spec/support/ and its subdirectories. Files matching `spec/**/*_spec.rb` are
# run as spec files by default. This means that files in spec/support that end
# in _spec.rb will both be required and run as specs, causing the specs to be
# run twice. It is recommended that you do not name files matching this glob to
# end with _spec.rb. You can configure this pattern with the --pattern
# option on the command line or in ~/.rspec, .rspec or `.rspec-local`.
#
# The following line is provided for convenience purposes. It has the downside
# of increasing the boot-up time by auto-requiring all files in the support
# directory. Alternatively, in the individual `*_spec.rb` files, manually
# require only the support files necessary.
#
# Dir[Rails.root.join('spec/support/**/*.rb')].each { |f| require f }
# Checks for pending migrations and applies them before tests are run.
# If you are not using ActiveRecord, you can remove this line.
# ActiveRecord::Migration.maintain_test_schema!
ActiveJob::Base.queue_adapter = :test
FactoryBot.rewind_sequences
Faker::UniqueGenerator.clear
RSpec.configure do |config|
# Remove this line if you're not using ActiveRecord or ActiveRecord fixtures
config.fixture_path = "#{::Rails.root}/spec/fixtures"
# If you're not using ActiveRecord, or you'd prefer not to run each of your
# examples within a transaction, remove the following line or assign false
# instead of true.
config.use_transactional_fixtures = true
# RSpec Rails can automatically mix in different behaviours to your tests
# based on their file location, for example enabling you to call `get` and
# `post` in specs under `spec/controllers`.
#
# You can disable this behaviour by removing the line below, and instead
# explicitly tag your specs with their type, e.g.:
#
# RSpec.describe UsersController, :type => :controller do
# # ...
# end
#
# The different available types are documented in the features, such as in
# https://relishapp.com/rspec/rspec-rails/docs
config.infer_spec_type_from_file_location!
# for paperclip
config.after(:suite) do
FileUtils.rm_rf(Rails.root.join('tmp', 'storage'))
# FileUtils.rm_rf("#{::Rails.root}/tmp/storage")
end
# Filter lines from Rails gems in backtraces.
config.filter_rails_from_backtrace!
# arbitrary gems may also be filtered via:
# config.filter_gems_from_backtrace("gem name")
end
# Adding headers to request helper
def sign_in_test_headers(user)
headers = {}
headers['ACCEPT'] = 'application/json'
headers['Authorization'] = 'Bearer ' + JsonWebToken.encode({user_id: user.id}).to_s
headers
end
Also change spec_helper.rb as well with below code:
todo-app/rails-api/spec_helper.rb
# frozen_string_literal: true
# This file was generated by the `rails generate rspec:install` command. Conventionally, all
# specs live under a `spec` directory, which RSpec adds to the `$LOAD_PATH`.
# The generated `.rspec` file contains `--require spec_helper` which will cause
# this file to always be loaded, without a need to explicitly require it in any
# files.
#
# Given that it is always loaded, you are encouraged to keep this file as
# light-weight as possible. Requiring heavyweight dependencies from this file
# will add to the boot time of your test suite on EVERY test run, even for an
# individual file that may not need all of that loaded. Instead, consider making
# a separate helper file that requires the additional dependencies and performs
# the additional setup, and require it from the spec files that actually need
# it.
#
# See http://rubydoc.info/gems/rspec-core/RSpec/Core/Configuration
RSpec.configure do |config|
# rspec-expectations config goes here. You can use an alternate
# assertion/expectation library such as wrong or the stdlib/minitest
# assertions if you prefer.
config.expect_with :rspec do |expectations|
# This option will default to `true` in RSpec 4. It makes the `description`
# and `failure_message` of custom matchers include text for helper methods
# defined using `chain`, e.g.:
# be_bigger_than(2).and_smaller_than(4).description
# # => "be bigger than 2 and smaller than 4"
# ...rather than:
# # => "be bigger than 2"
expectations.include_chain_clauses_in_custom_matcher_descriptions = true
end
# rspec-mocks config goes here. You can use an alternate test double
# library (such as bogus or mocha) by changing the `mock_with` option here.
config.mock_with :rspec do |mocks|
# Prevents you from mocking or stubbing a method that does not exist on
# a real object. This is generally recommended, and will default to
# `true` in RSpec 4.
mocks.verify_partial_doubles = true
end
# This option will default to `:apply_to_host_groups` in RSpec 4 (and will
# have no way to turn it off -- the option exists only for backwards
# compatibility in RSpec 3). It causes shared context metadata to be
# inherited by the metadata hash of host groups and examples, rather than
# triggering implicit auto-inclusion in groups with matching metadata.
config.shared_context_metadata_behavior = :apply_to_host_groups
config.before(:suite) do
# reindex models
# User.reindex
# Restaurant.reindex
# Dish.reindex
# Country.reindex
# Service.reindex
# Job.reindex
# Conversation.reindex
# Booking.reindex
# Review.reindex
# and disable callbacks
# Searchkick.disable_callbacks
end
# config.around(:each, search: true) do |example|
# Searchkick.callbacks(true) do
#
# end
# end
# The settings below are suggested to provide a good initial experience
# with RSpec, but feel free to customize to your heart's content.
# # This allows you to limit a spec run to individual examples or groups
# # you care about by tagging them with `:focus` metadata. When nothing
# # is tagged with `:focus`, all examples get run. RSpec also provides
# # aliases for `it`, `describe`, and `context` that include `:focus`
# # metadata: `fit`, `fdescribe` and `fcontext`, respectively.
# config.filter_run_when_matching :focus
#
# # Allows RSpec to persist some state between runs in order to support
# # the `--only-failures` and `--next-failure` CLI options. We recommend
# # you configure your source control system to ignore this file.
# config.example_status_persistence_file_path = "spec/examples.txt"
#
# # Limits the available syntax to the non-monkey patched syntax that is
# # recommended. For more details, see:
# # - http://rspec.info/blog/2012/06/rspecs-new-expectation-syntax/
# # - http://www.teaisaweso.me/blog/2013/05/27/rspecs-new-message-expectation-syntax/
# # - http://rspec.info/blog/2014/05/notable-changes-in-rspec-3/#zero-monkey-patching-mode
# config.disable_monkey_patching!
#
# # Many RSpec users commonly either run the entire suite or an individual
# # file, and it's useful to allow more verbose output when running an
# # individual spec file.
# if config.files_to_run.one?
# # Use the documentation formatter for detailed output,
# # unless a formatter has already been configured
# # (e.g. via a command-line flag).
# config.default_formatter = "doc"
# end
#
# # Print the 10 slowest examples and example groups at the
# # end of the spec run, to help surface which specs are running
# # particularly slow.
# config.profile_examples = 10
#
# # Run specs in random order to surface order dependencies. If you find an
# # order dependency and want to debug it, you can fix the order by providing
# # the seed, which is printed after each run.
# # --seed 1234
# config.order = :random
#
# # Seed global randomization in this process using the `--seed` CLI option.
# # Setting this allows you to use `--seed` to deterministically reproduce
# # test failures related to randomization by passing the same `--seed` value
# # as the one that triggered the failure.
# Kernel.srand config.seed
end
Now rails is fully initialized, so we restart the whole project again as last time:
docker-compose down -v
docker-compose up --build -dGit Commit:
For committing to the git, we must remove git from rails folder as parent folder will be used in git which has docker-compose file. So, in terminal write:
rm -rf rails-api/.gitCreate User Model
To generate a user model, write in terminal:
docker-compose run rails-api rails g model User email:string password_digest:stringpassword_digest is the column in which user encrypted password will be saved.
Change user.rb model file with following code:
todo-app/rails-api/app/models/user.rb
require 'bcrypt'
class User
include BCrypt
include Mongoid::Document
# Schema
field :email, type: String
field :password_digest, type: String
# Validations
validates :email, presence: true, uniqueness: true, format: { with: /\A([^@\s]+)@((?:[-a-z0-9]+\.)+[a-z]{2,})\z/i }
validates :password, length: {minimum: 8, maximum: 72}, if: :password_required?
def password
@password ||= Password.new(password_digest)
end
def password=(new_password)
@password = Password.create(new_password)
self.password_digest = @password
end
private
# is password required for user?
def password_required?
password_digest.nil? || !password.blank?
end
end
Here we will take password field from the user and convert to encryption using bcrypt. Moreover, this file includes basic validations of email and password before saving.
Change the factory of user with the following code:
todo-app/rails-api/spec/factories/users.rb
FactoryBot.define do
factory :user do
email { Faker::Internet.unique.email }
password { "abcd@1234" }
end
endThis will create a new unique email every time we create a user during testing
We will write a simple test of validation by validating factory generated user in user model testing file:
todo-app/rails-api/spec/models/user_spec.rb
require 'rails_helper'
RSpec.describe User, type: :model do
it "has a valid factory" do
user = FactoryBot.build(:user)
expect(user.valid?).to be_truthy
end
endTo run test of the app write in terminal:
docker-compose run rails-api bundle exec rspecOr if you want to use spring while running RSpec for faster testing add gem spring-commands-rspec in development group and run the following command to init this for just one time.
docker-compose run rails-api bundle exec spring binstub rspecThereafter, you can always run rspec suite by running the following command:
docker-compose run rails-api bin/rspecHope everything will run smoothly else compare your code with GitHub codebase mentioned above.
Create SignUp SignIn Mutations of GraphQL:
User Type
To generate user type in GraphQL of rails run the following command:
docker-compose run rails-api rails g graphql:object userThis will create a file name user_type.rb fill it with following content:
todo-app/rails-api/app/graphql/types/user_type.rb
module Types
class UserType < Types::BaseObject
field :id, ID, null: false, description: "MongoDB User id string"
field :email, String, null: false, description: "User's email"
end
endWe want to output only ID which is string in case of mongodb and email of the user not the encrypted password.
Furthermore, we need to create input type of the user which will ask for user email and password during sign up or sign in mutation. So, create a folder named inputs in the types folder and a file named sign_in_input.rb with the following content:
todo-app/rails-api/app/graphql/types/inputs/sign_in_input.rb
module Types
module Inputs
class SignInInput < BaseInputObject
argument :email, String, required: true, description: "User's Email"
argument :password, String, required: true, description: "Password minimum 8 and maximum 72 characters long"
end
end
end
The same input will be used for sign up and sign in.
JWT library:
We need to create jwt library for creating an authentication token for authenticating user while using API by creating a jwt library which is placed in lib folder with name json_web_token.rb
todo-app/rails-api/lib/json_web_token.rb
class JsonWebToken
SECRET_KEY = "SECRET_KEY" # put your secret key here
def self.encode(payload, exp = 1.year.from_now) # change expiry of token by entering exp time here
payload[:exp] = exp.to_i
JWT.encode(payload, SECRET_KEY)
end
def self.decode(token)
decoded = JWT.decode(token, SECRET_KEY)[0]
HashWithIndifferentAccess.new decoded
end
end
Sign-Up Sign-In Mutation:
Now change the base mutation as we will have that authenticate user methods there.
todo-app/rails-api/app/graphql/mutations/base_mutation.rb
module Mutations
class BaseMutation < GraphQL::Schema::Mutation
null false
end
endNow create a folder named auth in mutations folder and create a file named sign_up.rb and add the following content:
todo-app/rails-api/app/graphql/mutations/auth/sign_up.rb
module Mutations
module Auth
class SignUp < BaseMutation
require 'json_web_token'
description "Sign Up the user into the system"
argument :input, Types::Inputs::SignInInput, required: true
field :token, String, null: false, description: "User's Authorizations Token to be used in Authenticated mutations and queries"
field :user, Types::UserType, null: false, description: "User output"
def resolve(input: nil)
user = User.new(email: input.email, password: input.password)
if user.save
token = JsonWebToken.encode({user_id: user.id})
if token
return {token: token, user: user}
else
raise GraphQL::ExecutionError.new("Server was unable to created token. Please try again later.")
end
else
raise GraphQL::ExecutionError.new(user.errors.full_messages.join(', '))
end
end
end
end
endSo, this will be a mutation that will have an input object with email and password as argument and return token that will contain user_id and the user type with id and email. If error comes, it will give graphql execution error.
Lastly, enable this mutation by adding following in mutation type of graphql:
todo-app/rails-api/app/graphql/types/mutation_type.rb
module Types
class MutationType < Types::BaseObject
# Auth
field :sign_up, mutation: Mutations::Auth::SignUp
end
endSimilarly, we will create sign in mutation:
todo-app/rails-api/app/graphql/mutations/auth/sign_in.rb
module Mutations
module Auth
class SignIn < BaseMutation
require 'json_web_token'
description "Signs In the user into the system"
argument :input, Types::Inputs::SignInInput, required: true
field :token, String, null: false, description: "User's Authorizations Token to be used in Authenticated mutations and queries"
field :user, Types::UserType, null: false, description: "User output"
def resolve(input: nil)
user = User.find_by(email: input.email)
if user && user.password == input.password
token = JsonWebToken.encode({user_id: user.id})
if token
return {token: token, user: user}
else
raise GraphQL::ExecutionError.new("Server was unable to created token. Please try again later.")
end
else
raise GraphQL::ExecutionError.new("Invalid Credentials Provided.")
end
end
end
end
endThis finds the user with email and verifies the password before giving token and have same arguments and fields as of sign up.
Enabling the sign-in in mutation type:
todo-app/rails-api/app/graphql/types/mutation_type.rb
module Types
class MutationType < Types::BaseObject
# Auth
field :sign_up, mutation: Mutations::Auth::SignUp
field :sign_in, mutation: Mutations::Auth::SignIn
end
endTesting Mutations with RSpec:
Now create a folder named graphql in spec and in that mutations and in that auth folder and create test spec by add following code to sign_up_spec.rb file:
todo-app/rails-api/spec/graphql/mutations/auth/sign_up_spec.rb
require 'rails_helper'
module Mutations
module Auth
RSpec.describe SignUp, type: :request do
describe '.resolve' do
it 'create a user and signs in the user' do
params = FactoryBot.attributes_for(:user)
query = <<~GQL
mutation {
signUp(input: {email: "#{params[:email]}", password: "#{params[:password]}"}) {
token
user {
id
email
}
}
}
GQL
post '/graphql', params: {query: query}
expect(response).to have_http_status(200)
json = JSON.parse(response.body)
expect(json["data"]["signUp"]["token"]).not_to be_nil
end
end
end
end
end
You can see here I am sending a GQL query that if resolved then must have a token in output.
Similarly, RSpec test for sign in will be:
todo-app/rails-api/spec/graphql/mutations/auth/sign_in_spec.rb
require 'rails_helper'
module Mutations
module Auth
RSpec.describe SignIn, type: :request do
describe '.resolve' do
it 'creates a user session' do
user = FactoryBot.create(:user)
query = <<~GQL
mutation {
signIn(input: {email: "#{user.email}", password: "abcd@1234"}) {
token
user {
id
email
}
}
}
GQL
post '/graphql', params: {query: query}
expect(response).to have_http_status(200)
json = JSON.parse(response.body)
expect(json["data"]["signIn"]["token"]).not_to be_nil
end
end
end
end
end
See and Test in Graphical GraphQL UI
Restart the server:
docker-compose down -v
docker-compose up --build -dRun http://localhost:3000/graphiql to run the playground in the browser.
You can see the results in the image below.
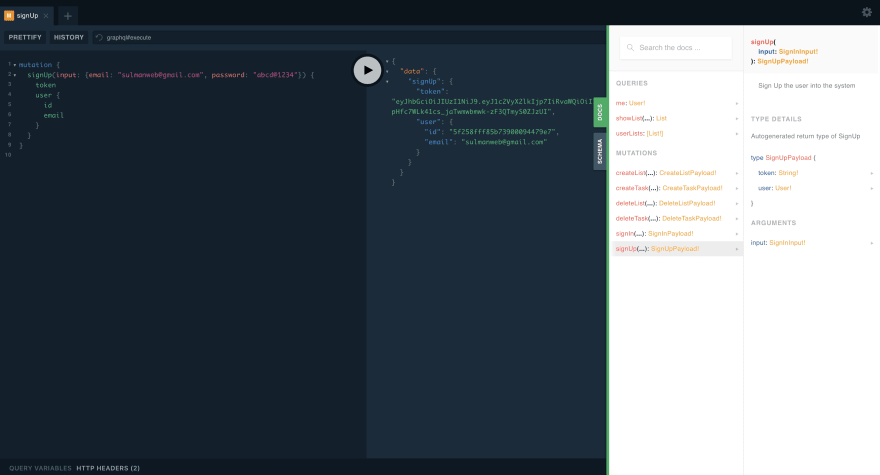
So by this little effort. We could create graphql api in rails with mongodb and beautiful ui for front end developers.
In the next part, I will create mutation and queries for user’s lists and to-dos.
Happy Coding!